Type of stamping
ü Type of stamping:
Stamping is mainly classified according to process and can be divided into
two major categories: separation process and forming process. Punching,
bending, shearing, stretching, bulging, spinning, and rectification are several
major stamping processes.
1. Separation process: Separation process is also
called blanking. Its purpose is to separate the stamped parts from the sheet
material along a certain contour and ensure the quality requirements of the
separation section.
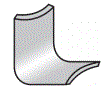
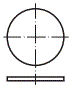
(1) Piercing: The
die is punched along the closed line, and the part that is punched is scrap.
Used for punching holes in flat or formed parts
Before processing
|
After processing
|
(2) Shearing: Cut
the sheet with scissors or a die, and the cut line is not closed. Mostly used
for processing simple flat parts
Before processing
|
After processing
|
(3) Blanking: The
die is punched along the closed line, and the punched part is the workpiece.
For the manufacture of various shapes of flat parts
Before processing
|
After processing
|
|
|
(4) Notching: Use
a notch mold to open part of the material without completely separating it, and
the material in the cut part is bent.
Before processing
|
After processing
|
|
|
2. Forming process: The purpose is to make the sheet
plastically deform without breaking the blank to produce a workpiece of the
desired shape and size. In actual production, a variety of processes are often
applied to one workpiece.
(1) Bending: The
metal sheet is machined so that it is bent to the desired shape and angle
within the range of plastic deformation. When the external force is removed, it
can maintain the permanent deformation of the bend, which is called bending
processing. This kind of processing can complete the general bending, curling,
twisting and other work. Bending is one of the main processes widely used in
the production of stampings.
Before processing
|
After processing
|
(2) Drawing: A
method of punching a hollow part in which a flat blank obtained after punching
is opened by a die. This kind of processing can complete the general pumping,
stretch forming and stealth work, can be made into cylindrical, stepped,
tapered, spherical, box-shaped and other irregularly shaped thin-walled parts.
Before processing
|
After processing
|
|
|
(3) Spinning: It
is a kind of metal rotary processing technology. During the processing, the
blank rotates actively with the spinning die or the spinning head rotates
around the blank and the spinning die. The spinning head performs the feeding
movement with respect to the mandrel and the blank, so that the blank is
continuously deformed locally to obtain the desired hollow rotation. Body
parts.
(4) Flanging: It is
a plastic processing method that bends the material of the narrow band region
of the edge of the prefabricated hole on the edge of the sheet blank or the
blank into a vertical edge along the curve or straight line. Flanging is mainly used to strengthen the edges of parts,
remove trimmings, make parts that are assembled and connected with other parts
on parts, or have three-dimensional parts with complex specific shapes and
reasonable space, and at the same time improve the
rigidity of parts. In the automotive, aerospace, aerospace, electronics
and household appliances and other industrial sectors have been widely used.
(5) Flattening/ Sizing: It is the second trimming of the shape of the product using the established
grinding shape. Mainly reflected in the pressure plane, bouncing feet and so
on. For some materials there is elasticity, can not guarantee the quality of a
molding, the re-processing.
(6) Bulging: It
is a kind of processing method that uses the mold to make the sheet stretched
and thinned to increase the surface area to obtain parts.
Before processing
|
After processing
|
|
|
(7) Necking: The
radial pressure from the outside to the inside of the hollow part is applied to
the mouth of the hollow part to reduce the local diameter.
ü 沖壓加工的種類:
沖壓主要是按工藝分類,可分為分離工序和成形工序兩大類。沖裁、彎曲、剪切、拉伸、脹形、旋壓、矯正是幾種主要的沖壓工藝。
1.
分離工序:分離工序也稱沖裁,其目的是使沖壓件沿一定輪廓線從板料上分離,同時保證分離斷面的質量要求
(1)
沖孔: 用模具沿封閉線沖切板料,衝下的部分為廢料。用於衝平板件或成形件上的孔
(2)
剪斷:用剪刀或模具切斷板料,切斷線不是封閉的。多用於加工形狀簡單的平板零件
(3)
落料: 用模具沿封閉線沖切板料,衝下的部分為工件。用於製造各種形狀的平板零件
(4)
剪切口:用切口模將部分材料開,不使它完全分離,切開部分材料發生彎曲。
2.
成形工序: 目的是使板料在不破坯的條件下發生塑性變形,製成所需形狀和尺寸的工件。在實際生產中,常常是多種工序綜合應用於一個工件。
(1)
彎曲:加工於金屬板料,使其在塑性變形範圍內,彎曲成所需要的形狀與角度,當外力除去時仍能維持其彎曲之永久變形,稱為彎曲加工。此種加工可以完成一般彎曲、捲邊、扭曲等工作。彎曲是衝壓件生產中廣泛採用的主要工序之一。
(2)
拉伸:是一種利用模具使沖裁後得到的平板坯料變成開口的空心零件的沖壓加工方法。此種加工可以完成一般抽製、伸展成形與隱身等工作,可以製成筒形、階梯形、錐形、球形、盒形和其他不規則形狀的薄壁零件。
(3)
旋壓:是一種金屬迴轉加工工藝。在加工過程中,坯料隨旋壓模主動旋轉或旋壓頭繞坯料與旋壓模主動旋轉,旋壓頭相對芯模和坯料作進給運動,使坯料產生連續局部變形而獲得所需空心迴轉體零件。
(4)
翻邊:是一種沿曲線或直線將薄板坯料邊部或坯料上預製孔邊部窄帶區域的材料彎折成豎邊的塑性加工方法。翻邊主要用於零件的邊部強化,去除切邊以及在零件上製成與其他零件裝配、連接的部位或具有復雜特異形狀、合理空間的立體零件,同時提高零件的剛度。在汽車、航空、航天、電子及家用電器等工業部門中得到十分廣泛的應用。
(5)
整形/校形:是利用既定的磨俱形狀對產品的外形進行二次修整。主要體現在壓平面、彈腳等。針對部分材料存在彈性,無法保證一次成型品質時,採用的再次加工。
(6)
脹形:是一種利用模具使板料拉伸變薄局部表面積增大以獲得零件的加工方法。
(7)
縮口:用模具對空心件口部施加由外向內的徑向壓力,使局部直徑縮小。















留言
張貼留言